다 쓴 객체 참조를 해제하라
JDK 8버전 Stack 코드 문제점
public class Stack {
private Object[] elements;
private int size = 0;
private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
public Stack() {
elements = new Object[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];
}
public void push(Object e) {
ensureCapacity();
elements[size++] = e;
}
public Object pop() {
if (size == 0)
throw new EmptyStackException();
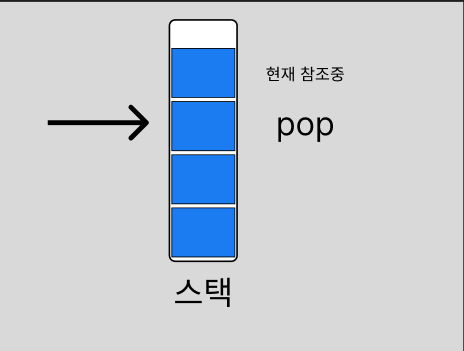
return elements[--size]; // 문제 발생!
}
private void ensureCapacity() {
if (elements.length == size)
elements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, 2 * size + 1);
}
}
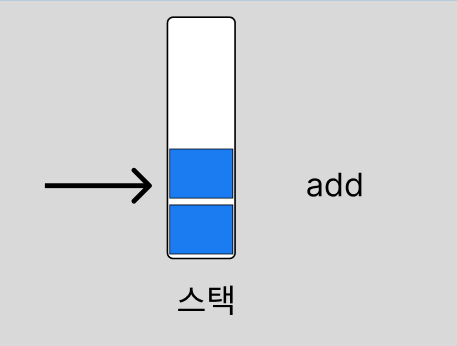
JDK 8버전에서는 현재 index를 변경해서 stack의 top을 관리하지만, pop()을 할 때 TOP의 값을 줄이기만 합니다. 이 부분에서 메모리 누수가 발생합니다.
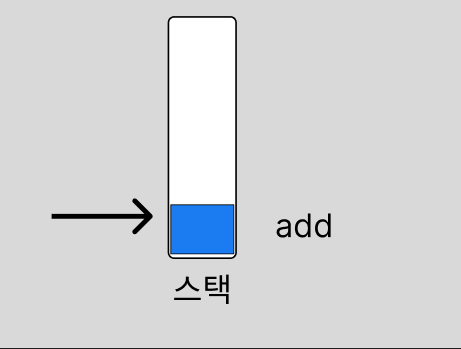
참조 무효화로 해결
public Object pop() {
if (size == 0)
throw new EmptyStackException();
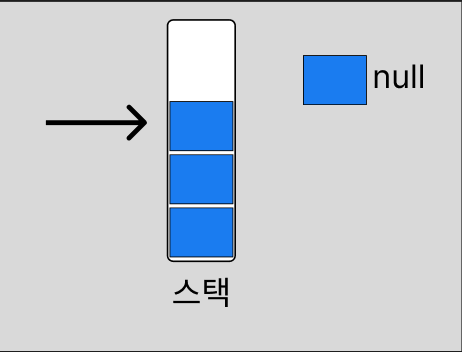
Object result = elements[--size];
elements[size] = null; // 참조 해제!
return result;
}
null 처리를 해주면 GC가 해당 객체를 정리합니다.
메모리 낭비를 줄이는 방법
1. 스코프 밖으로 밀어내라
public void test() {
if (true) {
Integer a = 10; // if문이 종료되면 변수가 해제
}
}
2. JDK 11 실제 Stack 구현부
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " + elementCount);
}
else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
modCount++;
elementCount--;
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
}
JDK 11버전에서는 null 처리를 통해 객체 참조 해제를 해줘서 Stack을 사용해도 메모리 누수로부터 안전합니다.
캐시 메모리 누수
객체 참조를 캐시에 넣고 제거하지 않으면 지속적인 참조 때문에 메모리 누수가 발생합니다.
Map<Object, String> map = new HashMap<>();
HashMap은 강한 참조 객체의 한 종류로, 직접적으로 key를 해제하지 않으면 메모리 누수가 발생합니다.
해결 방안: WeakHashMap
Map<Object, String> map = new WeakHashMap<>();
WeakHashMap을 사용하면 외부에서 해당 key 객체가 살아있는 동안만 key-value가 살아있습니다 (약한 참조). 단, key가 상수 풀에 저장되어 있으면 적용되지 않습니다 (예: primitive type).
예시 코드
HashMap
public static void hashMap() {
HashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
Integer num1 = new Integer(10);
String str1 = new String("str1");
Integer num2 = new Integer(20);
String str2 = new String("str2");
map.put(num1, str1);
map.put(num2, str2);
System.out.println(map.toString()); // {10=str1, 20=str2}
num1 = null;
System.gc();
System.out.println(map.toString()); // {10=str1, 20=str2} - 여전히 존재
}
WeakHashMap
public static void weakHashMap() {
WeakHashMap<Integer, String> map = new WeakHashMap<>();
Integer num1 = new Integer(10);
String str1 = new String("str1");
Integer num2 = new Integer(20);
String str2 = new String("str2");
map.put(num1, str1);
map.put(num2, str2);
System.out.println(map.toString()); // {10=str1, 20=str2}
num1 = null;
System.gc();
System.out.println(map.toString()); // {20=str2} - 10이 사라짐
}
WeakHashMap은 key를 참조 해제했을 때 key가 사라진 것을 볼 수 있으며, HashMap은 강한 결합 때문에 key를 가지고 있어 메모리 누수가 발생할 수 있습니다.
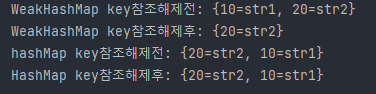
참조
- 이펙티브 자바